
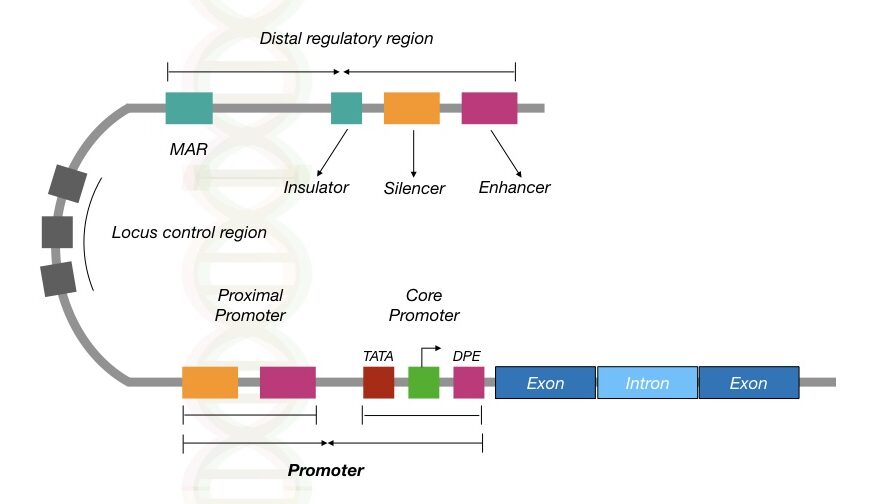
Issues with microarrays include cross-hybridization artifacts, poor quantification of lowly and highly expressed genes, and needing to know the sequence a priori. Prior to RNA-Seq, gene expression studies were done with hybridization-based microarrays. Other examples of emerging RNA-Seq applications due to the advancement of bioinformatics algorithms are copy number alteration, microbial contamination, transposable elements, cell type (deconvolution) and the presence of neoantigens. Recent advances in RNA-Seq include single cell sequencing, in situ sequencing of fixed tissue, and native RNA molecule sequencing with single-molecule real-time sequencing. RNA-Seq can also be used to determine exon/ intron boundaries and verify or amend previously annotated 5' and 3' gene boundaries. In addition to mRNA transcripts, RNA-Seq can look at different populations of RNA to include total RNA, small RNA, such as miRNA, tRNA, and ribosomal profiling. Specifically, RNA-Seq facilitates the ability to look at alternative gene spliced transcripts, post-transcriptional modifications, gene fusion, mutations/ SNPs and changes in gene expression over time, or differences in gene expression in different groups or treatments.
RNA-Seq (named as an abbreviation of RNA sequencing) is a sequencing technique which uses next-generation sequencing (NGS) to reveal the presence and quantity of RNA in a biological sample at a given moment, analyzing the continuously changing cellular transcriptome. This data can be used to annotate where expressed genes are, their relative expression levels, and any alternative splice variants. These sequences can then be aligned to a reference genome sequence to reconstruct which genome regions were being transcribed. The ds-cDNA is sequenced using high-throughput, short-read sequencing methods. The mRNA is extracted from the organism, fragmented and copied into stable ds-cDNA (blue). Within the organism, genes are transcribed and (in an eukaryotic organism) spliced to produce mature mRNA transcripts (red).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
